_________________________________________________________________________________________________
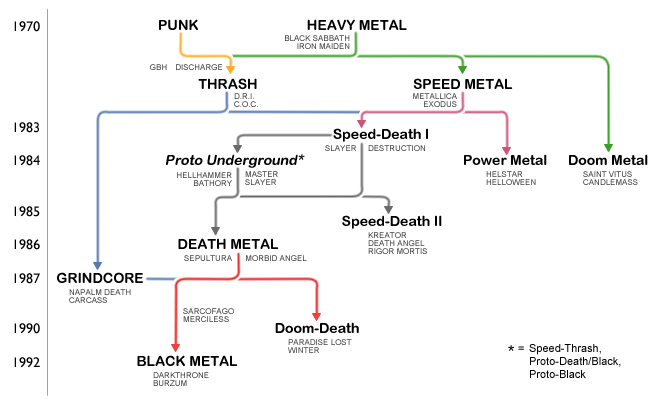
Structuralist, atonal, modal metal that combines hardcore punk compositional technique with metal riffs and song structure. “Only death is real,” its guiding statement, pointed out that most of social mores and morals are illusory, and that we need to pay attention to the structure of reality instead. Its specialty is seeming random until you hear the piece as a whole.
Demigod – Dead Soul
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
Lawless romanticism that praised isolation from the crowd, denial of individuality in the face of nature, natural selection, war and conflict, this genre used melody to construct atmospheric emotion. It guiding statement might well have been “the cut worm forgives the plough,” and its feral explosion left murders and mayhem across two continents.
Darkthrone – En As I Dype Skogen
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
Punk technique applied to neoclassical heavy metal with the use of muffled strumming made the most enigmatic heavy music ever, thanks to the use of the muted strum which produced a buffeting, battering sound. This was closest to heavy metal in composition but began the evolution of the phrasal riff as used in death metal.
Nuclear Assault – Nuclear War
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
Heavy metal riffs in punk song structures, with a combination of the epic view of history that metal favors with the punk anarchist criticism, resulting in one long questioning of the experiential value of modern society and its impact on people, especially teenage skateboarders (“thrashers,” hence the name). Many songs under thirty seconds; direct ancestor of grindcore.
Cryptic Slaughter – Nuclear Future
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
Progressive rock, Celtic folk and heavy rock forged this genre from the ruins of pop music, designed to sound like a horror movie and shock flower children into reality. Its innovation was the moveable power chord riff, creating for the first time rock compositions made of phrases and not based around open chords to which vocals harmonize.
Candlemass – A Sorcerer’s Pledge
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
Grindcore combined thrash, hardcore punk and death metal vocals to create a blur of intensity whose goal was to sound muddy, offtime, semi-coherent and like an ugly churning manifestation of the outsider underworld. Incorporating the organic post-political concepts of death metal, many grindcore bands expressed themselves through lyrics about gore, death and other limits to human control.
Blood – Linear Logic Intelligence
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
 Other Music
Other Music
Other genres influenced metal as it evolved. Ranging from ambient music, horror film soundtracks, punk hardcore, industrial noise and progressive rock, metal’s many influences are documented here, with an emphasis on those that reflected a paradigm shift in their time and passed that on, through their music and ideas, to metal out of compatibility with the spirit of metal.
King Crimson – One More Red Nightmare
No CommentsTags: To do: music review links & mp3 samples